PCB vs PCBA: What’s the Difference and Why Does It Matter?
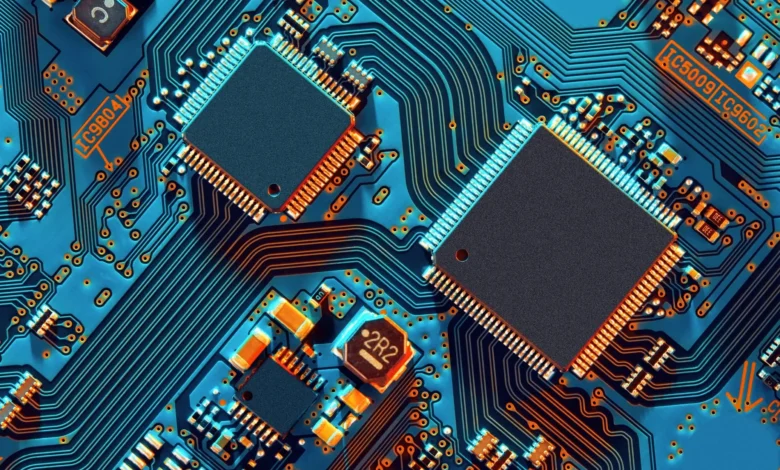
When dealing with electronics, the terms PCB (Printed Circuit Board) and PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) are commonly thrown around, but they are often misunderstood or used interchangeably. While they are related, they represent different stages in the production of electronic devices. Understanding the distinction between PCB and PCBA is crucial for manufacturers, engineers, and anyone involved in electronics design or assembly.
What is a PCB?
A PCB is the physical base of any electronic device, and it’s what connects and supports the various components of the circuit. Essentially, it’s a board made from non-conductive material (like fiberglass or epoxy), with copper traces that act as electrical pathways for the components. Think of the PCB as the “skeleton” of an electronic device—without it, the components wouldn’t be able to function or communicate with each other.
PCBs can be found in virtually all modern electronic devices, ranging from smartphones and computers to home appliances and medical equipment. They come in different types—single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer—depending on the complexity of the device.
Key Characteristics of PCBs:
- Base Structure: Typically made of fiberglass or composite resin.
- Conductive Paths: Copper traces that form the connections between components.
- Manufacturing Process: Involves etching, drilling, and applying solder mask.
- Purpose: Provides the platform for components to be mounted and electrically connected.
See also: Green Pest Control: Natural Methods To Keep Your Home Critter Free
What is PCBA?
Once the PCB is created, it’s still not functional. For it to become operational, it needs to be populated with electronic components like capacitors, resistors, ICs, and connectors. This process is known as PCBA, which stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly.
PCBA refers to the complete process of attaching components to the bare PCB, which involves techniques such as surface-mount technology (SMT), through-hole technology (THT), or a combination of both. Once all components are securely soldered into place, the PCBA is tested to ensure proper functionality and performance.
Unlike a PCB, a PCBA is not just a passive piece of material—it’s a fully functional and tested assembly that is ready for use in a final product.
Key Characteristics of PCBAs:
- Assembly Process: Includes placing and soldering components to the PCB.
- Techniques: Can use surface-mount, through-hole, or mixed methods.
- Testing: PCBA undergoes testing to verify its functionality, including functional, in-circuit, and sometimes X-ray inspections.
- Final Product: A fully operational circuit board ready to be integrated into a larger system.
The Major Differences Between PCB and PCBA
Why Does the Difference Matter?
Understanding the difference between PCB and PCBA is essential for both designers and manufacturers. If you are in the early stages of product development, you may only need to source a PCB, which serves as the foundation. However, if you are looking to create a fully functional electronic device, you will need to go further and opt for a PCBA—the complete assembly of components on the PCB.
For manufacturers, knowing whether you need a PCB or a PCBA helps streamline the process. Companies that specialize in PCB fabrication focus on creating the bare boards, while those in the PCBA sector handle the assembly of components onto those boards. Some manufacturers might even offer both services, allowing clients to get a fully assembled and tested board in one go.
When Do You Need PCB vs. PCBA?
The choice between PCB and PCBA depends on the stage of development and the product you are creating. If you are designing a prototype, you might initially work with just a PCB to test your circuit design before adding components. Once you are ready for full-scale production, you will need to transition to PCBA to ensure your board works as intended.
For products that will require multiple iterations or designs with various functionalities, PCBA is the way to go, as it ensures your device will perform correctly once the components are mounted.
Conclusion
Both PCB and PCBA play indispensable roles in electronics manufacturing, but they serve distinct purposes. The PCB is the platform on which electronic components are mounted, while the PCBA is the finished product, where all components are integrated and tested to ensure functionality. Understanding these differences is essential for anyone involved in designing, manufacturing, or assembling electronic devices. By recognizing when you need a PCB versus a PCBA, you can better navigate the manufacturing process and ensure your product is both functional and reliable.






